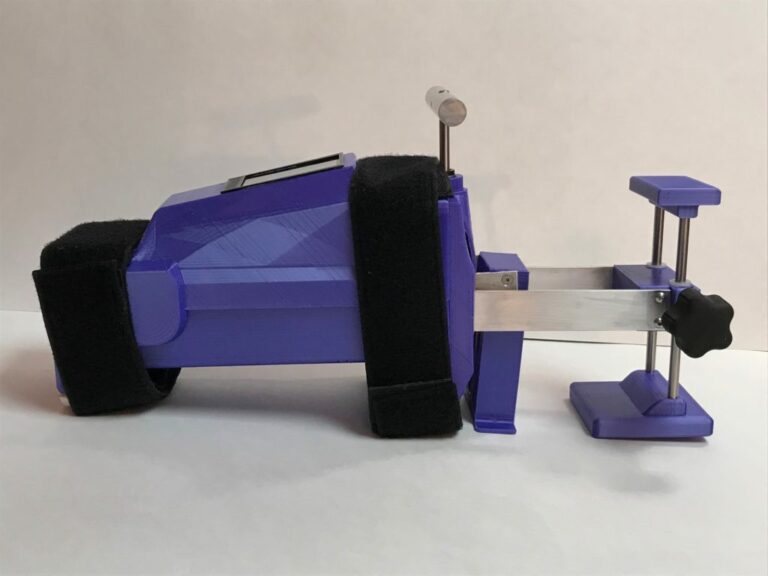
Diagnose ACL Injuries
using the
Blue Bay
Knee Arthrometer
The Blue Bay Medical Knee Arthrometer provides a reliable, quantitative, radiation-free method for measuring knee laxity.
Interpreting Data – ACL
The measured difference between the right and left knee in most individuals with no knee injuries is less than 3 mm. An ACL deficient knee will most likely result in a right/left knee difference of greater than or equal to 3 mm.
Interpreting Data – PCL
A normal knee will move slightly posterior from 0.5 to 2 mm. A PCL deficient knee will result in an anterior shift of the tibia 2 mm or more.
Diagnose ACL Injuries
using the
Blue Bay
Knee Arthrometer
The Blue Bay Medical Knee Arthrometer provides a reliable, quantitative, radiation-free method for measuring knee laxity.
Interpreting Data – ACL
The measured difference between the right and left knee in most individuals with no knee injuries is less than 3 mm. An ACL deficient knee will most likely result in a right/left knee difference of greater than or equal to 3 mm.
Interpreting Data – PCL
A normal knee will move slightly posterior from 0.5 to 2 mm. A PCL deficient knee will result in an anterior shift of the tibia 2 mm or more.

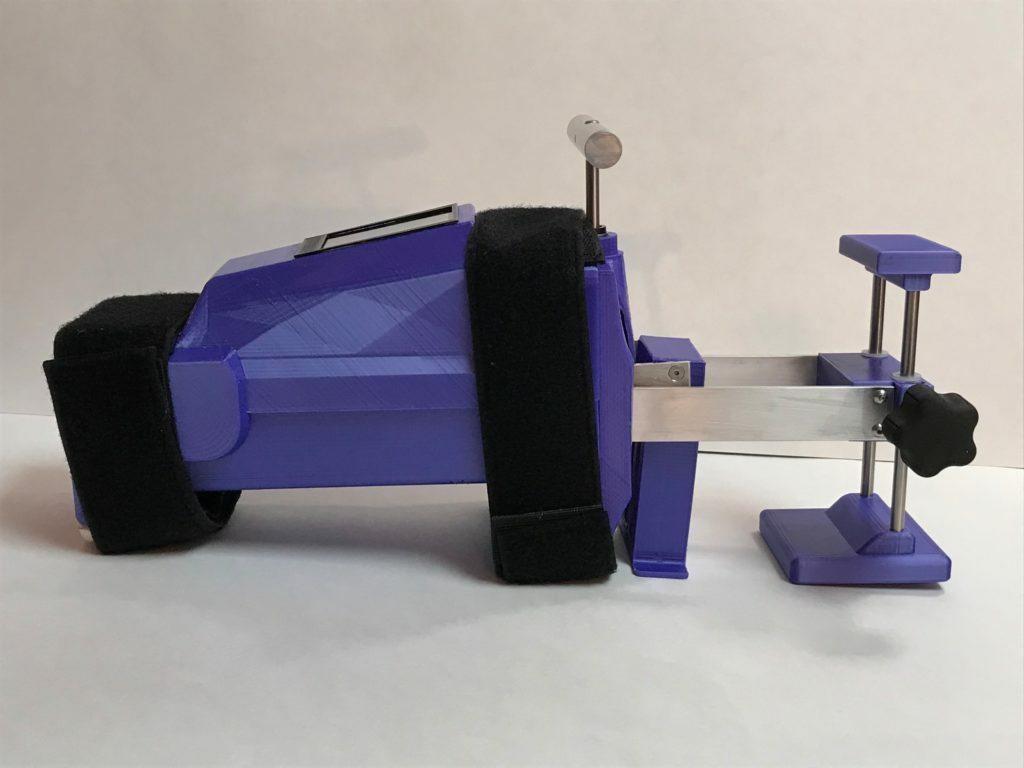
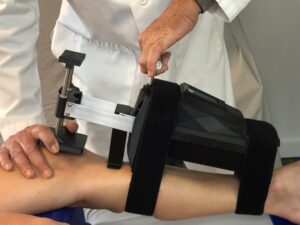
Measuring Knee Laxity
The Blue Bay KA is designed to measure the anterior-posterior placement of the tibia relative to the patella. This is to aid in diagnosis of knee cruciate ligament injuries (ACL and PCL). The KA is indicated for use in providing a quantitative assessment of knee laxity in anterior-posterior loading.
Measuring Knee Laxity
The Blue Bay KA is designed to measure the anterior-posterior placement of the tibia relative to the patella. This is to aid in diagnosis of knee cruciate ligament injuries (ACL and PCL). The KA is indicated for use in providing a quantitative assessment of knee laxity in anterior-posterior loading.